Review of MCAT Free Full-Length Sample Test
Biological and Biochemical Foundations of Living Systems
Missed Questions
Question 4 Subcategory: Cellular biology
Key concept: Proteins, once created, usually follow these steps:
Cytoplasm -> endoplasmic reticulum -> Golgi apparatus -> cell membrane
Retrograde transport from the Golgi to the ER occurs when proteins that cycle between the ER and Golgi must be retrieved.
Question 8 Subcategory: Organs and organ systems
Key concept: When given the choice between different treatments, choose the one that will prevent the symptom from occurring, rather than attacking the results of the symptom.
Example: Which is preferred treatment for opioid addiction, Narcan or naltrexone?
Answer: Naltrexone would be preferred because it prevents the harmful symptom (overdose) from occurring.
Question 9 Subcategory: Organs and organ systems
Key concept: Repeated use of xeno-antibodies, such as mouse antibodies, in the same patient will elicit the production of human anti-mouse antibodies over time.
For more details on this, look up the HAMA response
Question 13 Subcategory: Central dogma
Key concept:
Stages of transcription
- Initiation -
- RNA polymerase binds to the promoter sequence at the beginning of the gene. Then, the enzyme unzips the DNA strands.
- Elongation - The template strand of DNA acts as a template while RNA plymerase builds a strand of complementary nucleotides. The mRNA strand grows from 5’ to 3’.
The RNA strand carries the same information as the non-template strand of DNA, but it contains uracil (U) instead of thymine (T).
-
Termination - A terminator sequence signals that the RNA strand is complete. Once transcribed, they cause release of the transcript.
-
Modification - In eukaryotic organisms, the transcript is only pre-mRNA. It must be modified before translation.
- The mRNA must add a 5’ cap at the beginning and a 3’ poly-A tail at the end. This increases the stability of the mRNA.
- It will often undergo splicing, where introns are cut out, leaving the exons stuck together. If introns are not removed, the resulting polypeptide will be faulty.
Question 15 Subcategory: Acid/base reactions
Key concept: The pH of blood is higher than that of pure water, usually around 7.4. This is maintained by other equilibria (buffers).
*Question 16** Biochem, I’ll do this later
Question 21 Subcategory: Central dogma
Key concept: Errors in translating proteins can result in mistranslation. Mistranslation most often results in misfolding of the protein.
Question 22 Subcategory: Organs and organ systems
Key concept: The control of blood sugar by insulin is the classic example of a negative feedback loop.
Blood sugar rises -> pancreas secretes insulin -> body cells take up glucose and liver creates glycogen -> homeostasis
Blood sugar falls -> alpha cells in pancreas release glucagon -> liver releases glucose via glycogenesis -> blood sugar risese to homeostasis
Question 23 Subcategory: Bioenergetics
Key concept: Under low-food conditions, where nutrients are at low concentrations, only the high affinity transporters of L-alanine would be able to facilitate its binding and uptake.
Question 31 Subcategory: Amino acids
Key concept: A zwitterion is a molecule that has both positive and negative regions of charge. Amino acids are zwitterionic at pH 7 because of their amino group and carboxyl group. This doesn’t seem to be much affected by the side chain.
Net charges of amino acids:
Negative: Aspartate, glutamate
Positive: Lysine, arginine, histidine
Neutral: all others
Question 35 Subcategory: Organs and organ systems
Key concept: Blood flows in the body from heart -> artery -> arteriole -> capillary -> venule -> vein.
The arteriole is like the intermediary between artery and capillary. It controls blood flow to the capillaries, and is important for vasoconstriction.
The venule is intermediary between capillary and vein. It merges capillaries to conduct to veins.
Question 36 Subcategory: Organs and organ systems
Key concept: When fewer visual pigment molecules are available to absorb light, eg. color weakness, the nervous system simply sends fewer signals of that color to the brain.
Question 39 Subcategory: Organs and organ systems
Key concept: The retina is the portion of the eye that contains light receptors. The iris is not directly involved.
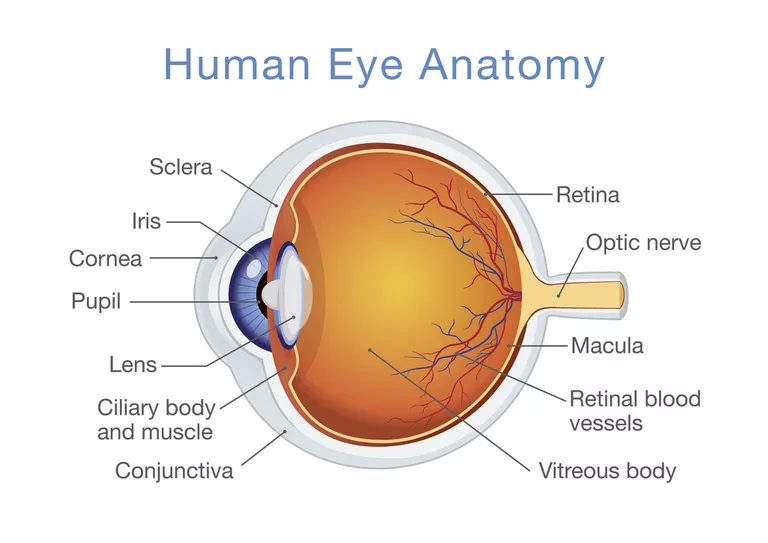
Other notes about the eye
- Light enters through the cornea, which acts as a lens to refract light
- Pupil dilates to adjust the amount of light that enters. When the pupil dilates, the cornea retracts.
- Retina is the coating on the interior back of the eye, which contains rods and cones
- Rods detect light/dark, work in dim, see motion, and are on the periphery
- Cones detect color, need brightness, located in the middle in the fovea
Question 40 Subcategory: Cellular biology
Key concept: ATP is manufactured in the mitochondria. This is why it is known as the fireplace of the cell.
As cells create ATP, they also produce heat, so this is how animals keep warm. Therefore cells that are involved in keeping warm will be rich with mitochondria.
Question 43 Subcategory: Organs and organ systems
Key concept: Just… read the damn questions correctly 😒
Question 47 Subcategory: Biochemistry
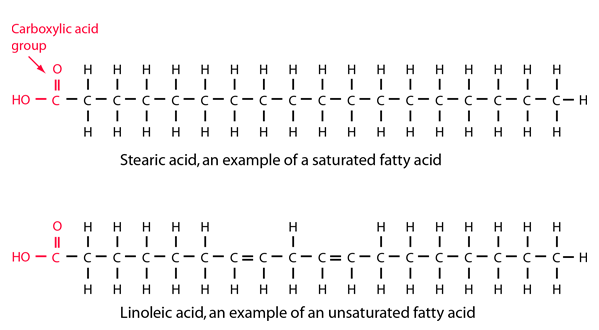
Key concept: A fatty acid is composed of a long hydrocarbon tail and a head consisting of a carboxylic acid group.
Question 55 Subcategory: Bioenergetics
Key concept: See this concept. Kd for an receptor-ligand is worse attachment and is in units of concentration. Ka is better affinity and is inverse-concentration units.
Question 57 Subcategory: Central dogma
Key concept: Transciption repressor protein will block transcription of a gene, transcription activator will promote transcription of a gene.
WOO!